
Calculate your rise and then your run! If your rise is downhill it is negative. where m is the slope of the line, (x 1, y 1) is a point on the line, and x and y are variables representing other points on the line.Point-slope form can be used when one point on the line and the slope are known.Slope is a fraction: rise/run. Point-slope form is one of the more commonly used forms of a linear equation, and has the following structure: y - y 1 = m(x - x 1). Detailed step by step solutions to your Trigonometric Equations problems online with our math solver and calculator.Point slope form.
#Slope intercept form equation maker plus#
2 nd method is the one that takes account of at least the coordinates of one point plus either the slope or the angle in incline. Also, its value can be zero, positive, negative, or undefined.Enter the coordinates (x1, y1), (x2, y2)of two points to calculate the values required. What is Slope? It is the amount of slant which the line has. As a result, it gives the Slope of Line passing through those points.

It takes two-dimensional coordinate points (x 1, y 1) and (x 2, y 2) as an input. Step 3: Click on the "Calculate" button to find the equation of a line.A slope calculator is an online geometry tool. Step 2: Enter the x1 x 1 and y1 y 1 coordinates as well as the slope in the given input boxes. Please follow the steps given below to find the equation of a line using the point slope form calculator: Step 1: Go to Cuemath's online point slope form calculator. First, label the points as x1 = 2, y1 = - 5, x2 = -2 and y2 = 4. So to find the slope of a line segment joining the points ( 2, - 5) and (- 2, 4). The slope formula of the line passing through the points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) can be found by: m = y2 −y1 x2 −x1. Example: To calculate the slope-intercept equation for a line that includesDwayne M. Statistics Probability College Calculus: Level I College Calculus: Level II Multivariable Calculus Linear Algebra Differential EquationsĬhemistry: General Chemistry Gen.To calculate the slope intercept form equation from two coordinates (x 1,y 1) and (x 2,y 2): Step 1: Calculate the slope (y 2 - y 1) / (x 2 - x 1) Step 2: Calculate where the line intersects with the y-axis by entering one of the coordinates into this equation: y - mx = b. Mathematics: Basic Math Pre Algebra Algebra I Algebra I Algebra II Geometry Trigonometry Precalculus Math Analysis AP Calculus AB AP Calculus BC AP Statistics Gen. Section 11: Rational Expressions and EquationsĪdding and Subtracting Rational Expressions with Like DenominatorsĪdding and Subtracting Rational Expressions with Unlike Denominators Section 10: Radical Expressions and Equations Solving Equations Using the Quadratic Formula Solving Equations by Completing the Square Inequalities: Multiplication and Division Techniquesįactoring Using Greatest Common Factor (GCF)įactoring Trinomials with Leading Coefficient 1 Inequalities: Addition and Subtraction Techniques Section 4: Linear Functions and their Graphs When the Variable is on Both Sides of the Equation Mathematics: Algebra 1 Section 1: Basic Concepts Then write the equation in slope-intercept form.
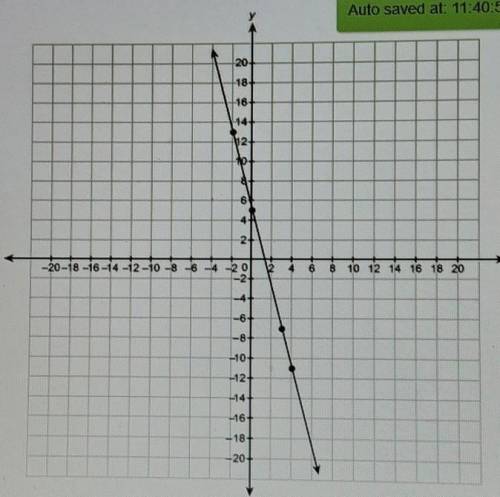
The follow the procedure just given to find the y-intercept you can use either point to do this.

If you are given 2 points that lie on a line, first use their coordinates to find the slope. Then you have the information necessary to write the equation in slope-intercept form. If you are given the slope of a line and a point that is not the y-intercept, first find the y-intercept by substituting the coordinates of the point and the given slope into the slope-intercept form and solving for b. In most problems involving linear equations and their graphs, you will be asked to find the equation in slope-intercept form.

If you are given the equation in slope-intercept form, you can use the information given by the equation to draw the graph without the need to create a table of values. Given a graph, you can determine the slope and the y-intercept and then write the equation in slope-intercept form. The slope-intercept form of a linear equation is y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept of the graph.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
